LPG Contains Which Gases? Gases Present in LPG – LPG in Gas
LPG – LPG Gas Composition: LPG Gas Mixture of Propane & Butane
LPG – Liquefied Petroleum Gas – composition is primarily propane, butane, and isobutane in a range of LPG in gas mixtures.
LPG – LPG gas is produced as a co-product of crude oil refining and natural gas processing. It is stored as LPG in gas bottles.
The constituents of LPG are gaseous at 20°C and 1 atmosphere pressure (NTP).
LPG – Liquefied petroleum gas or liquid petroleum gas, also denoted as just propane or butane, are both flammable hydrocarbon gases used as fuel for LPG heating gases, cooking and vehicular fuel.
LPG – LPG gas is both propane and butane.
As butane does not vaporise (turn from liquid to gas) well at colder temperature, LPG suppliers typically add propane to the percentage of propane and butane in LPG.
Propane has a lower boiling point, at -42° vs -0.4°C for butane. So, propane will continue to vaporise in colder climates.
Compared in gaseous volume, butane does have a higher energy content at 111.4MJ/m³ vs propane at 93.2MJ/m³. Natural gas is only 38.7MJ/m³.
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG or LP gas) is also referred to by its constituent names – propane or butane. LPG are hydrocarbon fuel gases used for LPG in gas heating, cooking, hot water and vehicles.
Most countries have LPG – LPG gas as either 100% propane (Australia & USA), LPG in gas mixture of 60:40 propane:butane (NZ & Belgium) or percentage of propane and butane in LPG around 35:65 propane:butane LPG in gas mixture (India, Spain & Hungary).
LPG Gas Constituents – What is LPG – LPG Gas Made Up Of?
LPG – LPG gas is made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms forming propane and butane whilst natural gas is made up of lighter methane.
LPG is made up of a group of flammable hydrocarbon gases that are liquefied through pressurisation and commonly used as fuel.
Natural gas can be liquefied cryogenically into LNG.
LPG is made up of a number of gases under the LPG products label, including propane, butane, isobutane and LPG in gas mixtures of these gases and are also referred to as natural gas liquids – NGL.
LPG – LPG gas is stored as LPG in gas vessels ranging from small BBQ gas bottles to larger gas cylinders and tanks.
Liquefied Petroleum Gas – LPG – constituents are primarily propane, butane, isobutane, butylene, propylene and LPG in gas mixtures of these gases.
LPG – LPG gas constituents are produced from crude oil reefing and natural gas processing.
They are liquid under pressure and gas at room temperature and pressure.
LPG in Gas Mixtures – Liquefied Petroleum Gas Mixture
A liquefied petroleum gas mixture (LPG in gas mixture) consists of flammable hydrocarbon gases that include propane, butane, isobutane and LPG in gas mixtures of the three gases.
The percentage of propane and butane of LPG in gas mixture ranges from 100% propane to 20% propane and 80% butane.
The chart below shows the LPG in gas mixture percentage of propane and butane in LPG for about 17 countries.
Here are some the reported percentage of propane and butane of LPG in gas mixtures for other countries.
Note that some countries use a more propane rich LPG in gas mixture, in the winter time, to assure proper vaporisation:
| Australia | 100:0 LPG mixture |
| Austria | 100:0 to 80:20 LPG in gas mixture |
| Belgium | 60:40 LPG in gas mixture |
| Czech Republic | 60:40 in winter, 40:60 in summer |
| Denmark | 70:30 LPG in gas mixture |
| Finland | 95:5 LPG in gas mixture |
| Greece | 20:80 LPG in gas mixture |
| Hungary | 40:60 LPG in gas mixture |
| Ireland | 100:0 LPG in gas mixture |
| Italy | 90:10 to 20:80 depending on season |
| New Zealand | 70:30 to 60:40 depending on season |
| Portugal | 92:8 LPG in gas mixture |
| Slovenia | 35:65 LPG in gas mixture |
| Spain | 35:65 LPG in gas mixture |
| Turkey | 50:50 to 30:70 depending on the season |
| United Kingdom | 100:0 Note:Butane is available separately |
| USA | 100:0 LPG in gas mixture |
Submissions of percentage of propane and butane in LPG corrections and data for additional countries are most welcome. Just send to blog@elgas.com.au.
Butane and Propane Ratio is Changed Depending on the Season
In some areas or countries, the ratio of butane and propane is changed depending on the season.
Propane’s biggest advantage is a lower boiling temperature, at -42° vs -0.4°C for butane.
So, propane will continue to vaporise – turn to gas – even in colder climates.
This is why the ratio of propane to butane may be increased during the winter season.
LPG Terminology Varies by Country
Propane or butane alone are LPG but LPG describes more than just one gas.
So, any of these gases or LPG in gas mixtures or these gases can be legitimately referred to as “LPG”.
However, in a given country, the term LPG – LPG gas is generally understood to be whatever the typical constituents are for that country.

For example, in Australia, we call it LPG but it is propane.
Autogas in Australia can be either pure propane or propane mixed with butane.
Other names include Liquefied Petroleum Gas, bottled gas, camping gas, LPG gas, BBQ gas, and LP gas.
In NZ, LPG is a propane-butane mix.
Alternatively, the term “LPG” may not be used at all, with the gas being referred to by the specific gas name.
This is the case in the USA, where LPG is just called “propane”.
In the UK, consumers have choices. LPG is referred to as either propane, butane or LPG, depending on what gas is present in the customer’s choice.
In other countries, they call it “GPL” or “GLP” instead of “LPG”, as the acronym is based on different languages and syntax.
For example, in French it is “gaz de pétrole liquéfié” or in Spanish it is “gas licuado de petróleo”.
Other Names for LPG – LPG Gas
What does LPG stand for? LPG is an acronym for either Liquefied Petroleum Gas or Liquid Petroleum Gas.
LPG goes by many other names and this can sometimes be confusing.
It is also called LPG Gas, LP Gas, Propane, BBQ Gas, Camping Gas or Autogas, as well as all of the other specific gas names.
LPG – LPG Gas as Propane
Propane is a flammable hydrocarbon gas liquefied through pressurisation.
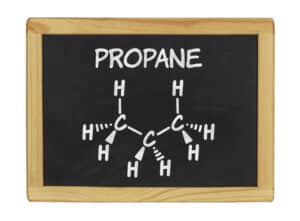
There are 3 carbon and 8 hydrogen atoms in a propane molecule.
The chemical formula for propane is C3H8. (Propane molecule model shown)
Propane is not made or manufactured, it is found naturally in combination with other hydrocarbons.
Propane is produced during natural gas processing and petroleum refining.
Propane processing involves the separation and collection of the gas from its petroleum base and other Natural Gas Liquids (NGLs).
Following its refinement, LPG – LPG gas is stored and distributed as a liquid under pressure until used, at which point it is utilised as either a liquid or a gas (vapour).
LPG is supplied in gas bottles that are either exchanged or refilled on site by LPG tankers.
Large users may utilise bigger LPG storage tanks.
Propane is the gas that is supplied to virtually all homes and most businesses that purchase LPG – LPG gas in Australia.
It is commonly used for LPG in gas heating and cooking.
Propane is frequently used in Autogas, alone or in a propane-butane mix.
LPG – LPG Gas as Butane
Butane (n-butane) is also considered to be LPG – LPG gas.
Butane is a flammable hydrocarbon gas that is liquefied through pressurisation.
The chemical formula for Butane is C4H10, with 4 carbon and 10 hydrogen atoms in a butane molecule. (Butane molecule model shown)
Butane comes from natural gas processing and oil refining.
Propane processing involves the separation and collection of the gas from its petroleum base and other Natural Gas Liquids (NGLs).
Following its refinement, LPG – LPG gas is stored and distributed as a liquid under pressure until used, at which point it is utilised as either a liquid or a gas (vapour).
It is used for LPG in gas heating and cooking, as well as auto fuel.
Butane is frequently used in Autogas in a propane-butane mix.
Butane is also used as a propellant and refrigerant, as well as a petrochemical feedstock.
Butane is supplied to businesses that require Butane, as opposed to propane.
Butane has some specific applications where it has advantages over propane.
LPG – LPG Gas as Isobutane
Isobutane (i-butane) is an isomer of butane, with the same chemical formula as butane but different physical properties.
Isobutane is converted from butane in a process called isomerization.
So, it has the same chemical formula as butane — C4H10 — but has a different arrangement of its atoms, as you can see in the 3-D model images. (Isobutane molecule model shown)
As with normal butane, isobutane is a flammable hydrocarbon gas that is liquefied through pressurisation.
It also has different physical properties from normal butane (n-butane).
In addition to being used as a fuel, isobutane is commonly used as a refrigerant and a propellant.
Isobutane has very low global warming potential and insignificant ozone depletion potential.
However, its main use is in refineries to increase octane of gasoline and make it cleaner burning.
LPG Properties Vary by the Specific Gas
As discussed, not all LPG gases are the same.
Different LPG gases have different physical properties and formulae.
LPG – LPG gas physical properties include specific gravity (density), boiling point, pressure, vapour expansion, energy content, combustion facts, flame temperature, flash point & more.
This chart shows some of the physical properties of the three most common LPG gases – propane, butane and isobutane…
| Gas Properties | Isobutane | Butane | Propane |
| Chemical Formula | C4H10 | C4H10 | C3H8 |
| Energy Content: MJ/m3 | 110.4 | 111.4 | 95.8 |
| Energy Content: MJ/kg | 45.59 | 47.39 | 49.58 |
| Energy Content: MJ/L | 25.0 | 27.5 | 25.3 |
| Boiling Temp: Cº | -11.75 | -0.4 | -42 |
| Pressure @ 21ºC: kPa | 310.9 | 215.1 | 858.7 |
| Flame Temp: Cº | 1975 | 1970 | 1967 |
| Expansion: m3/L | 0.234 | 0.235 | 0.270 |
| Gas Volume: m3/kg | 0.402 | 0.405 | 0.540 |
| Relative Density: H2O | 0.60 | 0.58 | 0.51 |
| Relative Density: air | 2.07 | 2.00 | 1.53 |
| L per kg | 1.669 | 1.724 | 1.96 |
| kg per L | 0.60 | 0.58 | 0.51 |
| Specific Gravity @ 25ºC | 2.06 | 2.07 | 1.55 |
| Density @ 15ºC: kg/m3 | 2.533 | 2.544 | 1.899 |
- Food: The Future of Food Starts Here: Paddock to Plate - February 25, 2026
- Bushfires & Gas Bottles: Safety Tips - January 9, 2026
- Sydney Gas Ban Explained: What It Means for New & Existing Homes - December 16, 2025