Butane – Butane Gas – Butane Chemical Formula- Butane Gas Canister

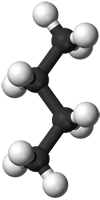 Butane (butane gas), with the chemical formula C4H10, is a highly flammable hydrocarbon gas that is both odourless and colourless.
Butane (butane gas), with the chemical formula C4H10, is a highly flammable hydrocarbon gas that is both odourless and colourless.
A butane gas molecule only contains four carbon and ten hydrogen atoms linked in a straight chain, which is also why it is called a hydrocarbon. (Butane gas molecule shown)
Liquid butane easily vaporises at normal ambient temperatures and pressures while butane gas liquefies readily under moderate pressure, in a butane gas canister or larger pressure vessels.
Butane (butane gas), along with propane gas, is LPG (liquefied petroleum gas).
It has many uses including as a fuel for automobiles, portable camping stoves (in a butane gas canister) and cigarette lighters, as an aerosol propellant, a refrigerant gas, heating and cooking fuel and as a petrochemical feedstock.
Butane Isomers
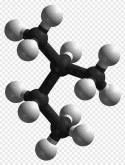 Butane exists as two isomers, which are n-butane when linked in a straight chain and isobutane when linked in a branched-chain. (model of isobutane molecule shown)
Butane exists as two isomers, which are n-butane when linked in a straight chain and isobutane when linked in a branched-chain. (model of isobutane molecule shown)
n-butane molecules have carbon atoms in a straight chain: CH3CH2CH2CH3
Isobutane molecules have carbon atoms in a branched configuration: (CH3)3CH
Isobutane (i-butane) is an isomer of normal butane (n-butane).
Isobutane formula – chemical formula of isobutane is C4H10.
Isobutane (isobutane gas) production is converted from butane (n-butane) in a process called isomerization.
This isomerization happens in something called a butamer unit (shown) and includes the use of platinum or another metal catalyst.
 In this isobutane production process, only some of the butane is actually converted to isobutane.
In this isobutane production process, only some of the butane is actually converted to isobutane.
After the butamer process, the output mixture goes through a fractionator or deisobutanizer tower that separates the unconverted butane from the isobutane production.
The isobutane (isobutane gas) production process rearranges the atoms into a different molecular configuration.
The component atoms of isobutane (isobutane gas) are the same but are arranged in a different geometric structure.
Butane Gas Flammability and Explosiveness – Butane Gas Limits of Flammability
Butane (butane gas) is extremely flammable and can form an explosive gas/air mixture with air when any source of ignition is present.
 Butane gas flame temperature is 1970°C or 3578°F.
Butane gas flame temperature is 1970°C or 3578°F.
Butane (butane gas) limits of flammability are 1.8% (LFL) to 8.5% (UFL) by volume, when mixed with air.
Assuming complete combustion, you get carbon dioxide and water:
2 C4H10 + 13 O2 → 8 CO2 + 10 H2O + Heat
However, with incomplete combustion you get carbon monoxide and water
2 C4H10 + 9 O2 → 8 CO + 10 H2O + Heat
This would typically occur if the ratio of oxygen to isobutane was insufficient.
Butane (Butane Gas) Propellant
 Hydrocarbons, like butane and isobutane, have been replacing chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) as aerosol propellants since the 1980’s.
Hydrocarbons, like butane and isobutane, have been replacing chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) as aerosol propellants since the 1980’s.
Butane (butane gas) is favoured for consumer and industrial aerosols because of its lower vapour pressure, at 215.1 kPa @ 21ºC.
Packaging typically refers to it as “hydrocarbon” as opposed to “butane”.
Butane Gas Refrigerants
 Butane (butane gas) is used as a refrigerant
Butane (butane gas) is used as a refrigerant
Butane gas refrigerant is known as R-600, where as isobutane refrigerant is known as R-600a (shown).
Both refrigerants have a low global warming potential (GWP) and are viewed as more environmentally friendly versus chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
There are also hydrocarbon mixtures of butane, isobutane and propane used as high-performance refrigerants.
Butane Boiling Point – Boiling Point for Butane & Isobutane Boiling Point: Butane Vaporisation
Butane boiling point (boiling point for butane) and isobutane boiling point are different, which is the temperature at which they go from liquid to gas (vapour).
Butane boiling point is at -0.4°C, whereas isobutane boiling point is at -11.75°C.
 When boiling, it looks like water boiling.
When boiling, it looks like water boiling.
This means you have a problem if you try to use pure isobutane when the temperature drops below -11.75°C or when the butane boiling point (boiling point for butane) is below -0.4°C.
No boiling and no vaporisation equals no gas.
So, when it gets cold, you could find yourself without gas (butane gas) for your heating and cooking appliances.
How is Butane Made – Butane (Butane Gas) Production

Butane (butane gas) is found in both natural gas wells and oil wells.
It is made during natural gas processing and crude oil refining.
Butane gas is separated from unprocessed natural gas using refrigeration, where it is butane in gas.
It is extracted from heated crude oil using a distillation tower.
Butane (butane gas) is stored pressurised, as a liquid butane, in gas cylinders or tanks.
Butane Gas & Isobutane Gas Properties
This chart shows some of the physical property differences between butane (butane gas) and isobutane gases.
| Butane Gas & Isobutane Gas Properties | ||
| Gas Properties | Butane (butane gas) | Isobutane |
| Chemical Formula | C4H10 | C4H10 |
| Energy Content: MJ/m3 | 111.4 | 110.4 |
| Energy Content: MJ/kg | 47.39 | 45.59 |
| Energy Content: MJ/L | 27.5 | 25.0 |
| Boiling Temp: Cº | -0.4 | -11.75 |
| Pressure @ 21ºC: kPa | 215.1 | 310.9 |
| Flame Temp: Cº | 1970 | 1975 |
| Expansion: m3/L | 0.235 | 0.234 |
| Gas Volume: m3/kg | 0.405 | 0.402 |
| Relative Density: H2O | 0.58 | 0.60 |
| Relative Density: air | 2.00 | 2.07 |
| L per kg | 1.724 | 1.669 |
| kg per L | 0.58 | 0.60 |
| Specific Gravity @ 25ºC | 2.07 | 2.06 |
| Density @ 15ºC: kg/m3 | 2.544 | 2.533 |
Note: Some numbers have been rounded.
Butane Gas FAQ
Butane Gas Bottle
A butane gas bottle is essentially the same as a propane gas bottle, only the contents vary.
Butane versus Propane - Propane v Butane
| Gas Properties | Butane | Propane |
| Chemical Formula | C4H10 | C3H8 |
| Energy Content: MJ/m3 | 111.4 | 95.8 |
| Energy Content: MJ/kg | 47.39 | 49.58 |
| Energy Content: MJ/L | 27.5 | 25.3 |
| Boiling Temp: Cº | -0.4 | -42 |
| Pressure @ 21ºC: kPa | 215.1 | 858.7 |
| Flame Temp: Cº | 1970 | 1967 |
| Expansion: m3/L | 0.235 | 0.270 |
| Gas Volume: m3/kg | 0.405 | 0.540 |
| Relative Density: H2O | 0.58 | 0.51 |
| Relative Density: air | 2.00 | 1.53 |
| L per kg | 1.724 | 1.96 |
| kg per L | 0.58 | 0.51 |
| Specific Gravity @ 25ºC | 2.07 | 1.55 |
| Density @ 15ºC: kg/m3 | 2.544 | 1.899 |
How to Fill a Butane Lighter?
- Make sure the lighter is completely empty before filling. Use the purging valve to do this.
- Turn the lighter completely upside down, so the bottom points straight up.
- Take you can of butane lighter fluid and invert it, with the fill tube pointing straight down.
- Insert the tube into the fill receptacle and press down to start the flow of butane (butane gas).
- You may wish to shake the can intermittently as you fill
- You’re done!
What is Butane (Butane Gas) ?
Butane gas (C4H10) is a highly flammable hydrocarbon gas that is both odourless and colourless.
It contains four carbon and ten hydrogen atoms linked in a straight chain.
Liquid butane vaporises at normal ambient temperatures and pressures while butane gas liquefies readily under moderate pressure.
How Do You Dispose of Butane Cans (Cylinders)? How to Recycle Butane Cans ?
Never dispose of a butane canister (butane can – butane cylinder) in general waste, as it could pose a hazard to trash collection and tip workers.
The best way to dispose of a butane canister (butane can) and recycle butane cans is by taking them to a Community Recycling Centre or one of your local household chemical clean-out events.
In Australia, many local councils run a Community Recycling Centre for the disposal and recycling of many household items, including butane canisters.
How Long Does a Butane Canister Last?
A 220g butane canister used in a, typical portable camping stove, will last for 1 to 3 hours.
The duration depends on the size of the burner, in MJ, the flame settings used, and the ambient temperature.
Obviously, the butane (butane gas) canister will last longer on lower flame settings.
As colder weather requires higher flame settings, this will adversely affect how long the butane canister will last.
Can You Refill Butane Canisters with Propane?
No, you cannot refill butane canisters with propane.
Propane has approximately 4x the vapour pressure of butane and about 2.75x the vapour pressure of isobutane.
Refilling butane canisters with propane would create a dangerous situation, as the camping stove is not designed for this higher pressure.
What is the Difference Between Butane Gas and Propane Gas?
The most important differences between butane (butane gas) and propane gas are a different boiling point and vapour pressure.
Propane boiling point is lower, at -42°C vs -0.4°C for butane boiling point.
So, propane will continue to vaporise – turn to gas – even in colder climates, down to -42°C vs butane boiling point at a higher -0.4°C.
Butane gas has a lower vapour pressure at a given temperature, being about ¼ that of propane gas.
This lower vapor pressure is advantageous for many propellant applications.
Is Butane a Gas?
Butane can be either a gas or a liquid,
Under pressure, in a butane canister or butane cylinder, butane exists as liquid butane.
When released under ambient pressure, the butane liquid vaporises into butane gas.
Where to Buy a Butane Canister?
In Australia, you can typically find butane canisters for sale at camping, BBQ, and hardware stores.
Are All Butane Canisters the Same?
The contents of butane canisters, where the contents are labeled as only butane, should always be the same.
Butane canisters and butane cylinders can vary based on size and method of attachment.
Are Butane Lighters Allowed on Airplanes?
Yes, you can take a single butane lighter on an airplane but with restrictions.
You cannot put the butane lighter in checked or carry-on luggage.
It must be carried on your person.
Note that butane canisters, used to refill butane lighters or for camping stoves, are NOT permitted.
Always check the rules of a specific airline, as their butane lighter restrictions may vary.
Can Butane be Used as a Refrigerant ?
Yes, butane (butane gas) is commonly used as a refrigerant, where it is referred to as R-600.
R- 600 butane refrigerant has very low global warming potential and insignificant ozone depletion potential.
Butane Chemical Formula
Butane Chemical Formula
The chemical formula for butane is C4H10
This is indicative of a molecule of butane composed of four carbon atoms and ten hydrogen atoms, all connected by single bonds.
Butane is an alkane, a type of hydrocarbon.
Molecular Formula is C4H10
Butane is composed of 4 carbon atoms and 10 hydrogen atoms
